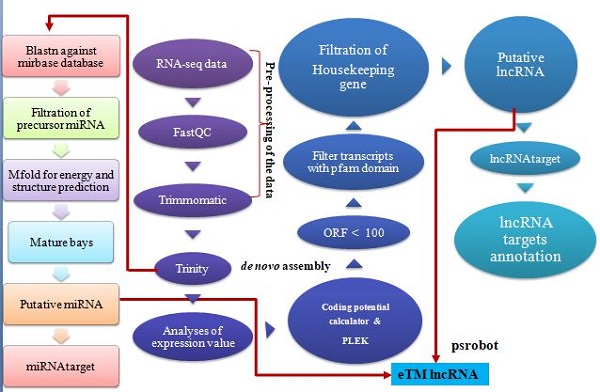
Fig.1.An integrative computational pipeline for the systematic identification of noncoding RNAs (lncRNA and miRNA) and their targets
|
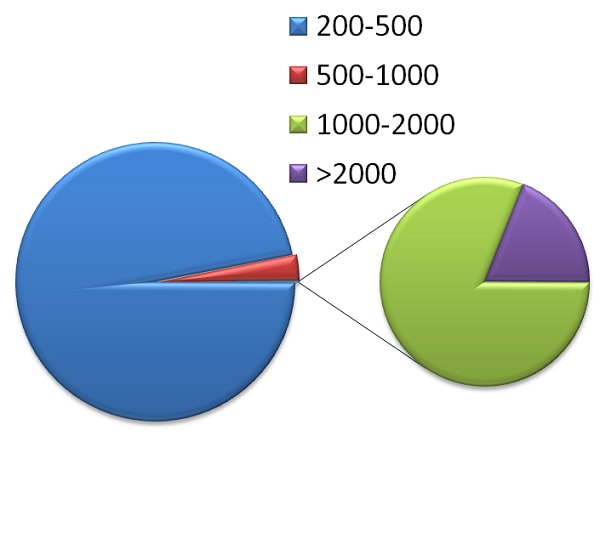
Fig.2.An integrative computational pipeline for the systematic identification of noncoding RNAs (lncRNA and miRNA) and their targets
|
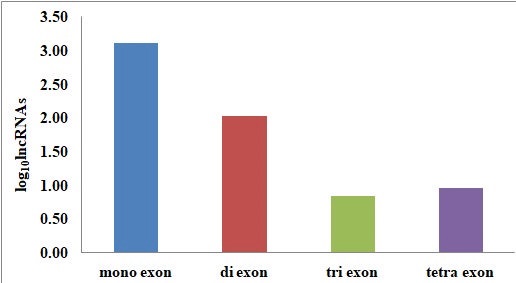
Fig.3.The characteristic feature of cluster bean lncRNA b) Distribution of exon on lncRNAs
|
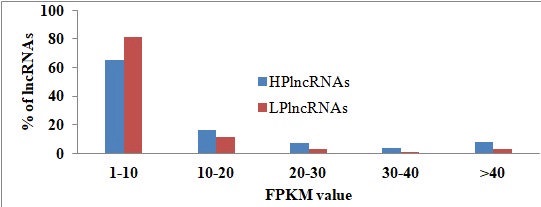
Fig.4.Categorization of HPlncRNA and LPlncRNA in cluster bean b) categorization on the basis of FPKM values
|
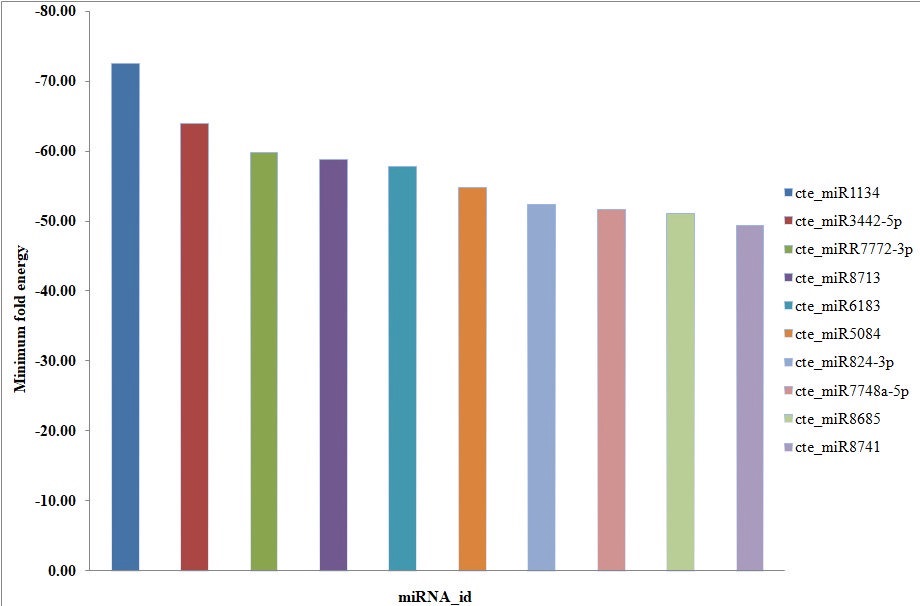
Fig. 5. Top ten most stable putative miRNAs of cluster bean showing MFE
|
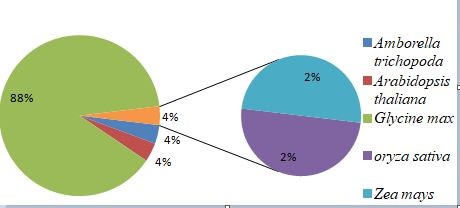
Fig.6.Conserverd cluster bean lncRNAs in different plant species
|
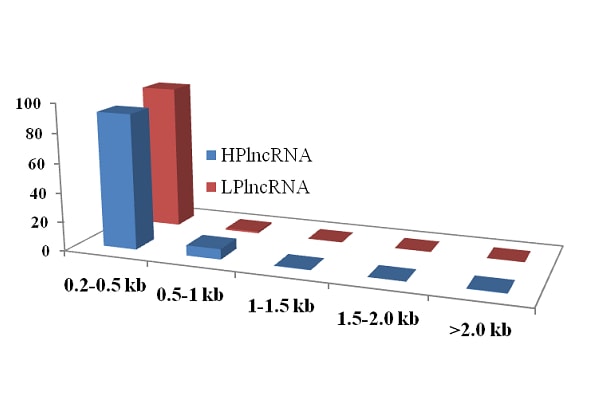
Fig.7.Categorization of HPlncRNA and LPlncRNA in cluster bean a) lengthwise categorization
|
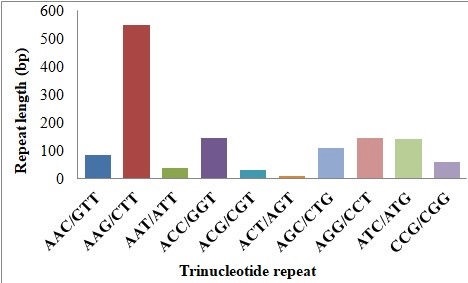
Fig.8.Categorization of HPlncRNA and LPlncRNA in cluster bean b) categorization on the basis of FPKM values
|
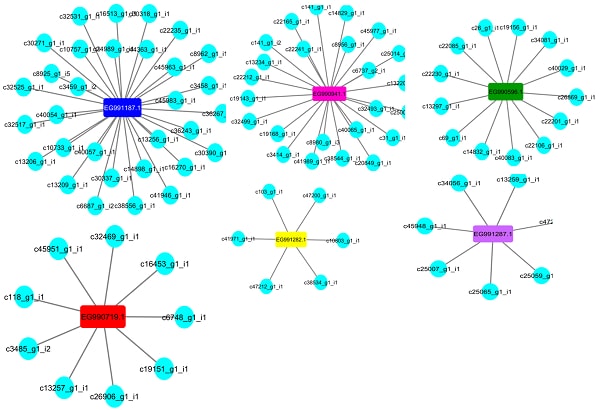
Fig.9.Representation of predicted interaction between lncRNA and expressed gene (EST). The ellipse and rectangular nodes represent lncRNAs and expressed gene respectively
|
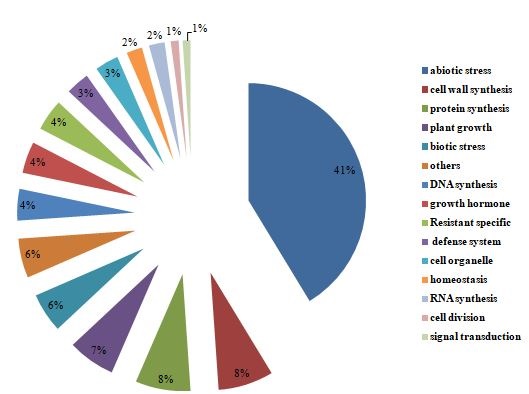
Fig.10.Functional annotation of targeted genes of cluster bean lncRNAs
|
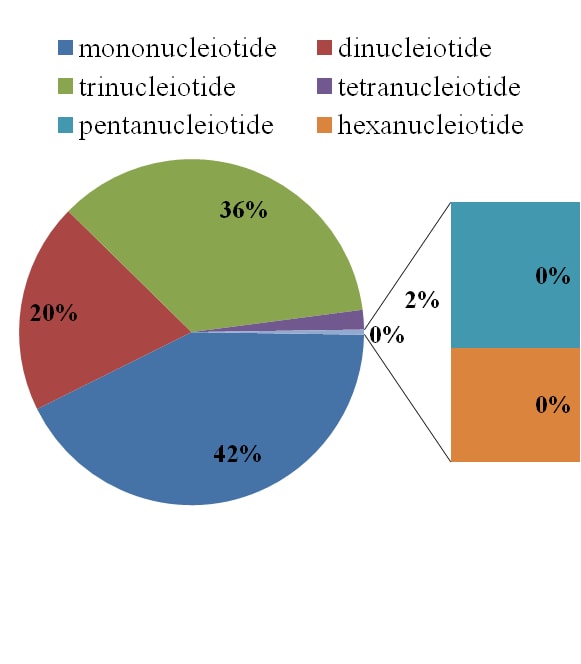
Fig.11. Simple sequence repeat analysis in cluster bean a) distribution of various type repeats
|

Fig.12 Predicted base pairing interaction between Endogenous target mimic (eTm) lncRNAs (red color) and miRNA (green color)
|